The efficiency of the Light Emitting Diode (LED) driver is the ratio of energy emitted by the driver to the power it consumes from the electric line. The higher the conversion efficiency, the higher the utilization rate of electric energy, which means that the power consumption is not so much; the higher the conversion efficiency, the lower the loss, and the less heat generated by the constant voltage led power supply.
Let’s express our definition in a simple formula;
LED Driver Efficiency = (output power/input power) * 100%
For example:
Load 100W lights = output power.
The input power is 120W.
Efficiency=(100W/120W)*100%=83%
Then the conversion efficiency of this power supply = 83%
Why is the efficiency of output voltage 12V and 24V different when calculating the led driver efficiency?
This is the law of physics. The higher the input voltage, the higher the conversion efficiency. The conversion efficiency is actually measured, so the data on the KSPOWER specification is relatively standard.
What Is Input Power?
Input power is the amount of energy that gets into a device or system. In this case, the device or system is the LED driver. The input power is the energy that comes into your electric bulb from the main supply. So what the LED driver will give out is highly dependent on the input power with the unit in watts.
What Is Output Power?
Output power is the amount of energy delivered by a device, circuit, or system.“what happens after the LED driver receives the energy (input power) from the electric line?” The best answer is that it supplies this power to the LED system.
Key Factors Affecting Efficiency
When we talk about efficiency, it will be an error not to consider its driving force. The efficiency of a LED driver hinges on the input voltage and load (output voltage).
Let’s take a look at the chart below:
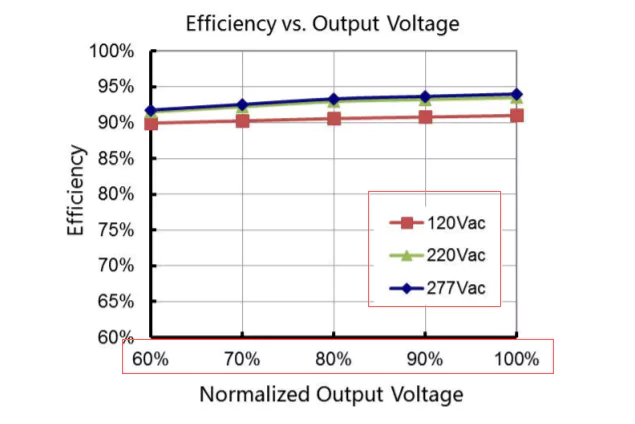
There are different power grids in the world. For example, we have 120 Vac and 277Vac for the North America and 220 Vac for most of other areas.
Looking at the chart, we can see that efficiency is different with both input voltage and output voltage which is also load in terms of a constant current LED driver.
Losses In Power Supply Efficiency
Energy losses occur in power supply; as a result, it’s impossible to have a 100% power supply. Active and passive component losses are the catalyst for energy loss in the power supply. The energy loss occurs in resistors, capacitors, inductors, diode conjunction, and (MOSFET)...
Passive Component Loss
Passive components are those part of the device that does not need the extra control signal to operate, including diodes, transformers, capacitors, inductors, and resistors.
Active Component Loss
In contrast to the passive components, active components need power for their operation. Therefore, they can produce power gain and amplify signals. The active components include a transistor, integrated circuit, SCR, MOSFET, etc.
Other Loss
Due to the existence of parasitic resistance of the components like PCB, cable, there are power loss occurring on the path through which the current goes.
Why Use High-Efficiency Driver?
Energy and Cost Saving
The first reason why you should use a high-efficiency driver is to save cost. Remember when the lighting will pull out significant money from your pocket due to high energy consumption. That’s why the whole industry turned towards LED lighting.
It’s an opportunity to take full advantage of cost savings with high-efficiency drivers. They require lesser energy input to provide the needed luminous output.
Increased Product Lifespan
The higher the driver’s efficiency, the lesser the heat it dissipates, and the longer the system’s life.
High Efficiency LED Driver
With up-to-date technology and practice, KSPOWER provides the following:
100-240VAC Input Power Adaptor
KSPOWER makes it all easy; you can get high-quality LED drivers with an outstanding 92% efficiency.